Failure to File Form 8833 Doesn't Waive Tie-Breaker Rule Benefits
Form 8833 requires prompt filing, but courts may still grant tax treaty benefits to non-residents despite failure to file timely, as this case shows.
File your 2025 FBAR correctly: Learn who must file, reportable accounts, step-by-step process, and penalty avoidance tips
Introduction: Understanding FBAR Reporting Requirements
The Foreign Bank Account Report (FBAR), or FinCEN Form 114, is a critical reporting requirement for U.S. persons with financial interests in or signature authority over foreign financial accounts. Suppose you have foreign bank accounts, investment accounts, or other financial holdings outside the United States that exceed $10,000 in aggregate at any point during the calendar year. In that case, you must file an FBAR with the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN).
FBAR compliance isn't merely a suggested practice—it's a mandatory requirement under the Bank Secrecy Act designed to combat tax evasion and money laundering through offshore accounts. With increased information sharing between financial institutions globally and heightened scrutiny from U.S. tax authorities, proper FBAR filing has never been more critical.
In this comprehensive guide, I'll walk you through the entire FBAR filing process, from determining your reporting obligations to submitting your FinCEN Form 114. Whether you're a first-time filer or seeking to ensure your existing compliance practices are current, this step-by-step approach will help you navigate the complexities of foreign account reporting and avoid potentially severe penalties.
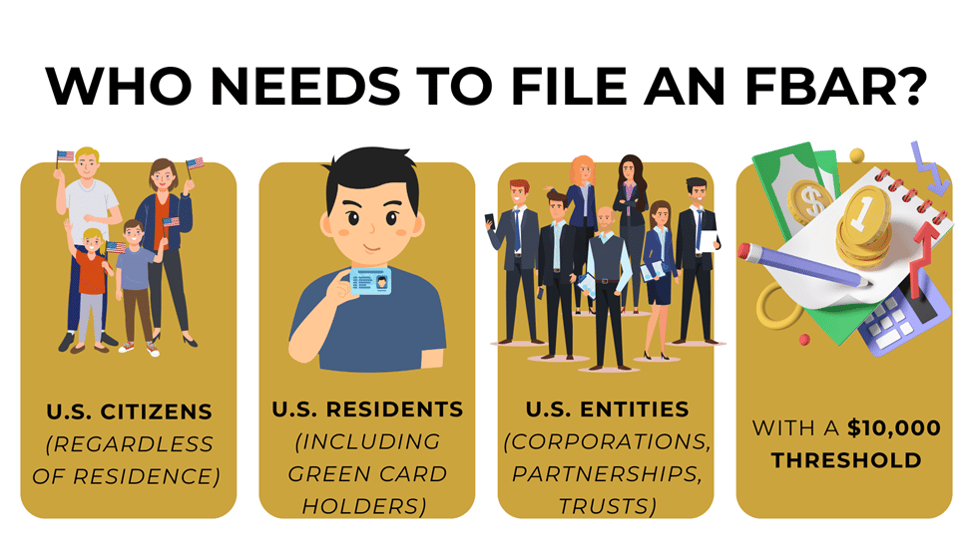
FBAR filing requirements apply to "U.S. persons," which include:
The definition is intentionally broad to capture all individuals and entities with potential foreign financial ties.
You must file an FBAR if the aggregate value of all your foreign financial accounts exceeds $10,000 at any time during the calendar year. This critical point catches many taxpayers off guard—the requirement is based on the combined maximum value of all accounts, not each account.
For example, if you have three foreign accounts with maximum balances of $4,000, $5,000, and $2,000, respectively, your aggregate maximum equals $11,000, exceeding the threshold and triggering the filing requirement. The combined value matters even if each account individually falls below $10,000.
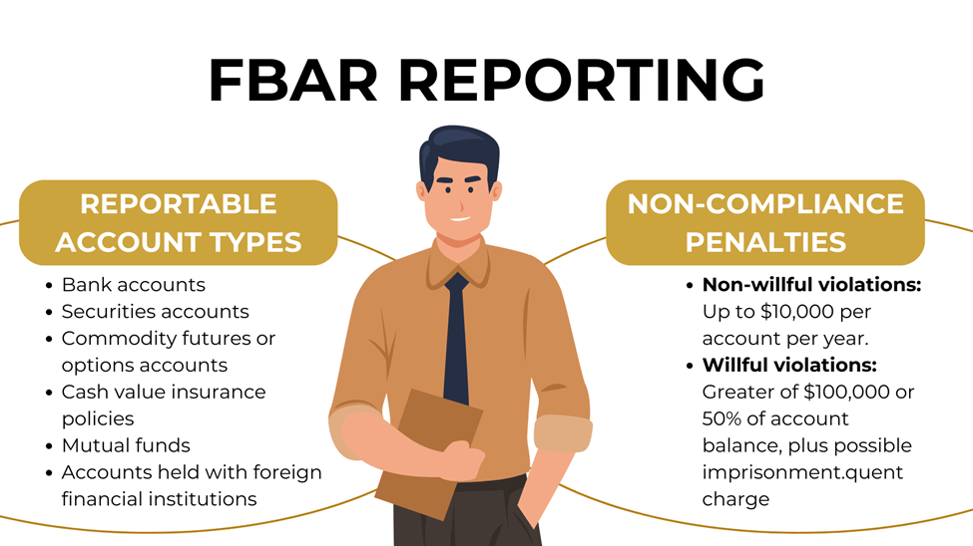
FBAR reporting covers a wide range of financial accounts held outside the United States:
Failing to meet FBAR filing obligations can result in substantial penalties that underscore the importance of compliance:
These penalties highlight why proper FBAR filing should be a priority for anyone with foreign financial accounts. Even if your foreign accounts generate no income or tax liability, the FBAR filing requirement still applies.
Before beginning the filing process, collect the following information for each foreign financial account:
3. Maximum value:
For each account, you'll need to report the maximum value during the calendar year converted to U.S. dollars:
FBAR filing must be done electronically through FinCEN's BSA E-Filing System:
Navigate through the form methodically to ensure all required information is properly reported:

Before submitting your FBAR:
After filing, maintain comprehensive records for at least five years from the due date:

Special Considerations for FBAR Filing
For U.S. persons with accounts in Southeast Asian countries, several unique considerations apply:
I recommend maintaining detailed records of how Southeast Asian accounts are categorized and valued to ensure consistent reporting across tax years.

If you've missed previous FBAR filing deadlines:
For the 2024 calendar year, FBAR filing is due April 15, 2025, with an automatic extension to October 15, 2025, without requiring a specific extension request. However, I recommend filing as soon as possible rather than waiting for the extension deadline, as early filing demonstrates good-faith compliance efforts.

Navigating FBAR filing requirements can seem daunting, but following this step-by-step guide will help ensure you meet your foreign account reporting obligations while minimizing the risk of costly penalties. Remember that the FBAR is filed separately from your tax return and has its own distinct requirements and deadlines.
Key takeaways for successful FBAR filing include:
At CHI border Tax Advisory, we specialize in helping U.S. persons navigate the complexities of international tax compliance. Our team can provide personalized guidance tailored to your specific circumstances.
Don't leave your FBAR compliance to chance. Schedule a complimentary consultation with Chi Border Tax Advisory today to ensure your foreign account reporting meets all requirements and protects you from potential penalties.

Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for general informational purposes only and should not be construed as professional tax advice. Tax laws and regulations are complex and subject to change. While we strive to provide accurate and up-to-date information, individual circumstances vary, and you should consult with a qualified tax professional regarding your specific situation.
Form 8833 requires prompt filing, but courts may still grant tax treaty benefits to non-residents despite failure to file timely, as this case shows.
When a Green Card Holder files I-407 mid-year, spouses can elect §6013(g) to file MFJ while Form 8854 uses the mid-year expatriation date. Steps,...
Navigating FBAR complexities can be daunting for cross-border individuals. Find out if you must file, understand the process, and avoid penalties.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to get the latest information. You can always unsubscribe from the newsletter.